The breechloading seven-shot, metallic-cartridge rifles invented by Christopher Miner Spencer were the most innovative and reliable repeaters of the conflict. The deadly weapons were the precursor to modern assault rifles.
Spencer was born in 1833, and grew up in Connecticut, a hotbed of industrial innovation. After cutting his gunmaking teeth working for Samuel Colt’s factory, Spencer left to develop his repeating rifle.

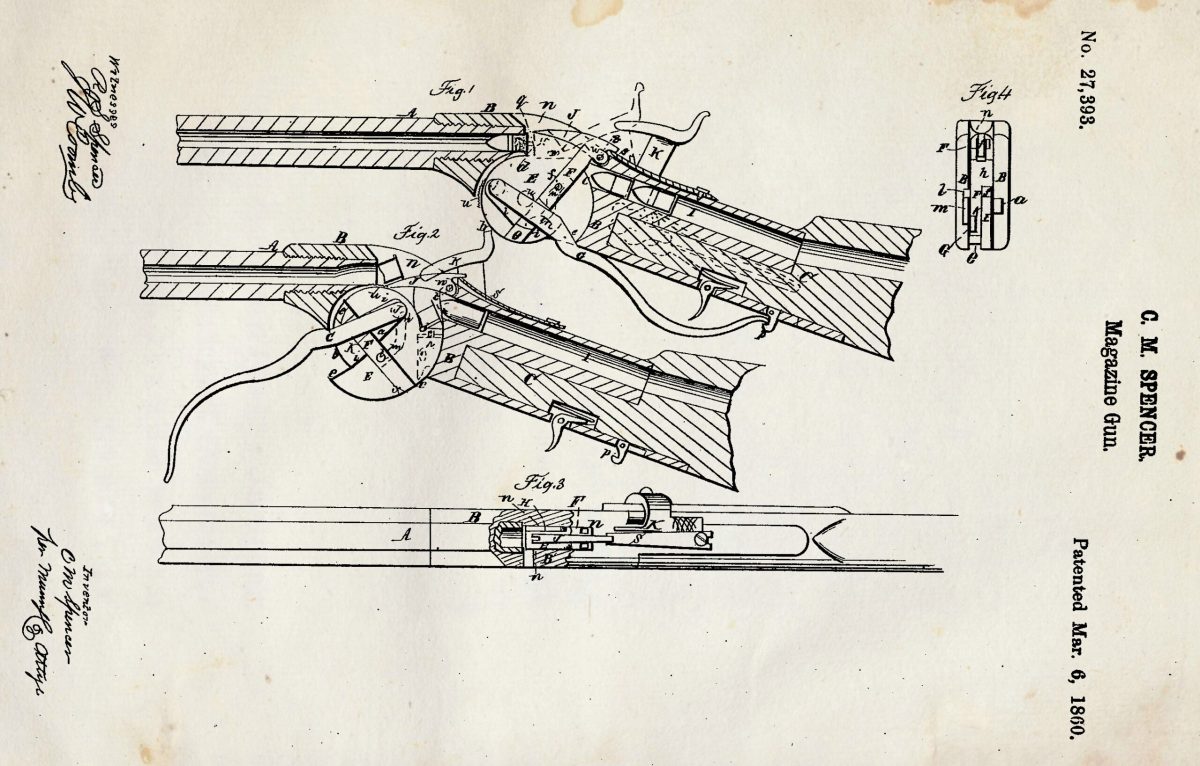
The inventor moved to Massachusetts, working in a silk mill by day and making drawings and wooden models of his firearm by night. After being satisfied his concept would work, he applied for and received a patent for his prototype in early 1860.
It’s a familiar story that the U.S. Army was hesitant to adopt new weapon technologies, and chose to rely on single-shot muzzle-loaders to arm the volunteer regiments that formed after the Civil War began.
Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles, however, was impressed with a demonstration of his repeater, and the Navy ordered 700 of them. Spencer then pressed his case all the way to President Lincoln, who ordered 10,000 in 1861. But it wasn’t until January 1863, when the weapons were in the hands of Union land troops. Four companies of Ohio sharpshooters were the first infantrymen to carry the weapon, and the 5th and 6th Michigan Cavalry used Spencer rifles to good effect at Gettysburg.
The gun’s reputation soared, and after Lincoln test fired a Spencer at the White House, their production and usage greatly increased. More than 200,000 were made at Spencer’s factory or under contract at the Burnside Rifle Company by 1869.
Spencer lived until 1922, long enough to see rapid-firing guns using metal cartridges dominating battlefields.